
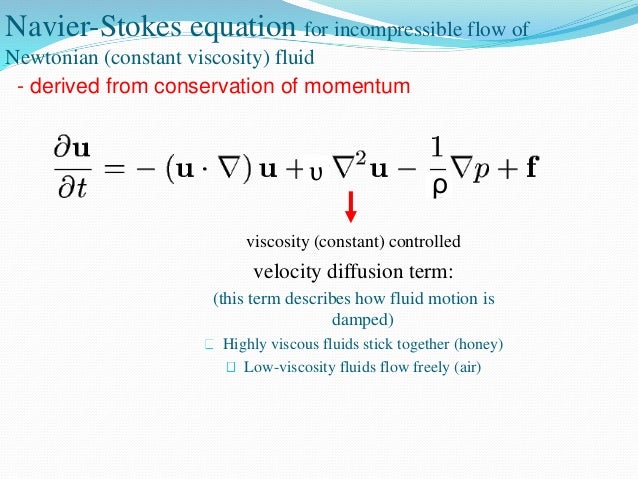
The next layer is in contact with the moving layer since there is internal friction between the two layers, it also accelerates, and so on through the depth of the fluid. The layer of fluid in contact with the moving plate is accelerated and starts to move due to the internal friction between moving plate and the fluid. In the diagram, the fluid is initially at rest. Fluids have zero shear strength, but the rate at which they are sheared is related to the same geometrical factors A and L as is shear deformation for solids. The motion in the figure is like a continuous shearing motion. Care is taken to ensure that the flow is laminar, that is, the layers do not mix. The greater the resistance to flow, the higher the viscosity, so in the previous example, the syrup has a higher viscosity than water. It can also be thought of as a measure of a fluid’s thickness or its resistance to objects passing through it. Each successive layer from the top down exerts a force on the one below it, trying to drag it along, producing a continuous variation in speed from v to 0 as shown. Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. Consider motion of this fluid along a solid boundary. The layer (or lamina) of fluid in contact with either plate does not move relative to the plate, so the top layer moves at speed v while the bottom layer remains at rest. Lets derive a mathematical description of viscosity: Consider fluid to be made of layers. The bottom plate is held fixed, while the top plate is moved to the right, dragging fluid with it.
The fluid to be measured is placed between two parallel plates. In the kinematic measuring method, gravity is the only force that acts on the sample.\) shows how viscosity is measured for a fluid.

The mass (or weight) of a fluid is determined by gravity. Therefore, we say that steel has a greater density than ice cube. Thus, water is 'thin', having alower viscosity, while honey is 'thick', having a higher viscosity. Ineveryday terms (and for fluids only), viscosity is 'thickness' or 'internal friction'. They may be the same size, but the steel cube weighs more than the ice cube. Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear stress or tensile stress. Think about an ice cube and a cube of steel.
Kinematic (cSt) x Density = Dynamic (cP).Density actually provides a way to convert between a kinematic and a dynamic viscosity measurement. The unit of measure of kinematic viscosity is Centistokes (cSt).Ī basic difference between the dynamic and kinematic viscosity measurements is density. The time is converted directly to kinematic viscosity using a calibration constant provided for the specific tube. There are several ways to find the kinematic viscosity of a fluid, but the most common method is determining the time it takes a fluid to flow through a capillary tube. Put another way, kinematic viscosity is the measure of a fluid’s inherent resistance to flow when no external force, except gravity, is acting on it. The other way is to measure the resistive flow of a fluid under the weight of gravity. One way is to measure a fluid’s resistance to flow when an external force is applied. Water at 20 ☌ has a kinematic viscosity of about 1 cSt. Other units are: 1 St ( Stoke) = 1 cm 2/s = 10 −4 m 2/s.

For isothermal flow, the viscosity can be considered constant in many cases. 3,428 Viscosity Formula Viscosity is measured in terms of a ratio of shearing stress to the velocity gradient in a fluid. At the boundary fluid velocity is zero and at uppermost layer it is some finite velocity. Lets derive a mathematical description of viscosity: Consider fluid to be made of layers. The SI unit of the kinematic viscosity is m 2/s. The absolute viscosity of many fluids relatively doesnt change with the pressure but very sensitive to temperature. FLUID MECHANICS 9,6&26,7< Resistance to motion in fluid. The kinematic viscosity is the ratio between the dynamic viscosity and the density of a fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
